适配器模式
李羽秋
2022年06月28日 · 阅读 1,517
适配器模式
1.概述
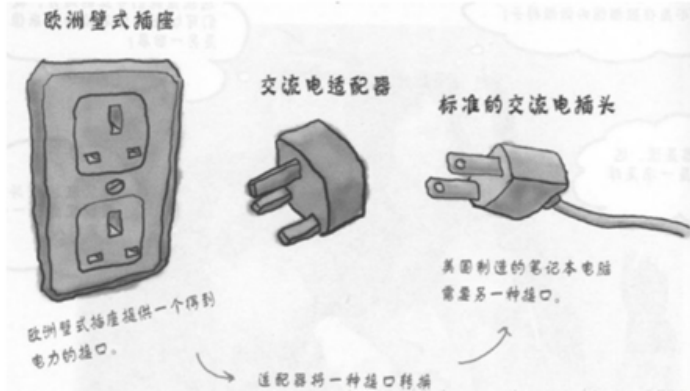
如果去欧洲国家旅游的话,他们的插座如下图最左边,是欧洲标准。而我们使用的插头如下图最右边的。因此我们的笔记本电脑,手机在当地不能直接充电。因此就需要一个插座转换器,转换器第一面插入当地的插座,第二面供我们充电,这样使得我们的插头在当地能使用。生活中的这样例子很多,手机充电器(将220v转换为5v的电压),读卡器等,其实就是是硬道理适配器模式。
定义
将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口,使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类能一起工作。
适配器模式分为适配器模式和对象适配器模式,前者类之间的耦合度比后者高,且要求程序员了解现有组件库中的相关组件的内部结构,所以应用相对较少些。
2.结构
适配器模式包含以下主要角色:
- 目标接口:当前系统业务所期待的接口,它可以是抽象类或接口
- 适配者类:它是被访问和适配的现存组件库中的组件接口。
- 适配器类:它是一个转换器,通过继承或引用适配者的对象,把适配者接口转换成目标接口,让客户按目标接口的格式访问适配者。
3. 类适配器模式
实现方式: 定义一个适配器类来实现当前系统的业务接口,同时又继承现有组件库中已经存在的组件。
例子:
现有一台电脑只能读取SD卡,而要读取TF卡中的内容的话就需要使用到适配器模式。创建一个读卡器,将TF卡中的内容读取出来。
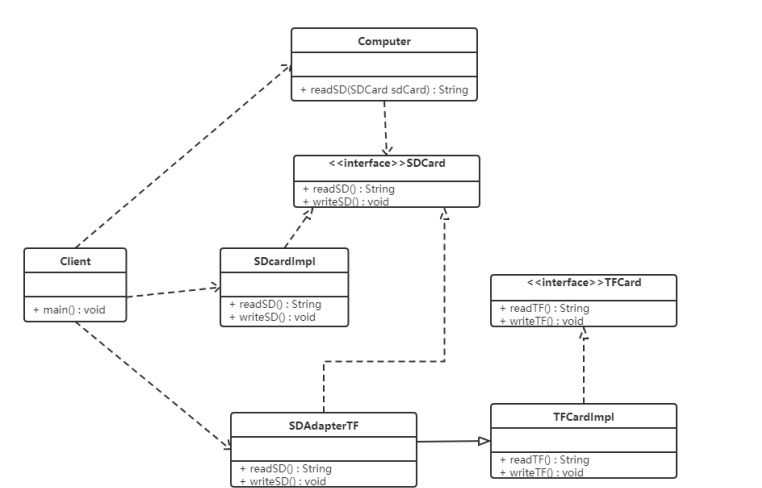
代码如下:
//SD卡的接口
public interface SDCard {
//读取SD卡方法
String readSD();
//写入SD卡功能
void writeSD(String msg);
}
--------------------------
//SD卡实现类
public class SDCardImpl implements SDCard{
@Override
public String readSD() {
String msg = "sd card read a msg :hello world so";
return msg;
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("sc card write msg :"+msg);
}
}
---------------------------
//电脑类
public class Computer {
public String readSD(SDCard sdCard){
if (sdCard == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("sd card null");
}
return sdCard.readSD();
}
}
-----------------------------
//TF卡接口
public interface TFCard {
//读取TF卡
String readTF();
//写入TF卡功能
void writeTF(String msg);
}
-----------------------------
//TF实现类
public class TFCardImpl implements TFCard{
@Override
public String readTF() {
String msg = "tf card read msg : hello world tf card";
return msg;
}
@Override
public void writeTF(String msg) {
System.out.println("tf card write a msg :" + msg);
}
}
-----------------------------
//定义适配器类(SD兼容TF)
public class SDAdapterTF extends TFCardImpl implements SDCard{
@Override
public String readSD() {
System.out.println("adapter read tf card");
return readTF();
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("adpter write tf card");
writeTF(msg);
}
}
----------------------------
//测试类
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer = new Computer();
SDCard sdCard = new SDCardImpl();
System.out.println(computer.readSD(sdCard));
System.out.println("-----------------");
SDAdapterTF adapter = new SDAdapterTF();
System.out.println(computer.readSD(adapter));
}
}
类适配器模式违背了合成复用原则,类适配器是客户类有一个接口规范的情况下可用,反之不可用。
4. 对象适配器模式
实现方式:对象适配器模式可采用将现有组件库中已经实现引入适配器类中,该类同时实现当前系统的业务接口。
例子:读卡器
我们使用对象适配器模式将读卡器的案例进行读写,类图如下:
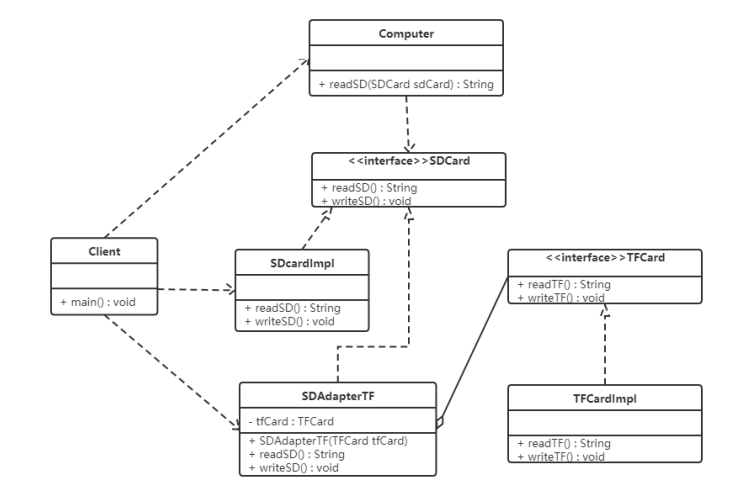
代码如下:
类适配器模式的代码,我们只需要修改适配器类和测试类
//创建适配器对象
public class SDAdapterTFTwo implements SDCard{
private TFCard tfCard;
public SDAdapterTFTwo(TFCard tfCard){
this.tfCard = tfCard;
}
@Override
public String readSD() {
System.out.println("adapter read tf card");
return tfCard.readTF();
}
@Override
public void writeSD(String msg) {
System.out.println("adapter write tf card");
tfCard.writeTF(msg);
}
}
------------------
//测试类
public class ClientTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer = new Computer();
SDCard sdCard = new SDCardImpl();
System.out.println(computer.readSD(sdCard));
System.out.println("------------------");
TFCard tfCard = new TFCardImpl();
SDAdapterTFTwo adapterTFTwo = new SDAdapterTFTwo(tfCard);
System.out.println(computer.readSD(adapterTFTwo));
}
}
5. 应用场景
- 以前开发的系统存在满足新系统功能需求的类,但其接口同新系统的接口不一致。
- 使用第三方提供的组件,但组件接口定义和自己要求的接口定义不同。
分类:
设计模式
标签:
无